SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS (STIs)
*What are STIs? * Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) – sometimes also called sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) – are diseases that are spread by sexual contact. STIs can cause severe damage to your body; even death. Except for colds and flu, STIs are the most common contagious (easily spread) infections in the world, with millions of new cases each year.
STIs affect both men and women, but in many cases the health problems they cause can be more severe for women. If a pregnant woman has an STI, it can cause serious health problems for the baby.
How are STIs transmitted?
A person with an STI can pass it to others through contact with skin, genitals, mouth, rectum, or bodily fluids. Anyone who has sexual contact – vaginal, anal, or oral sex – with an infected person, may get an STI. Some STIs, such as hepatitis, can also be transmitted without sexual contact, by coming into contact with an infected person’s blood. Others, such as gonorrhoea, can only be transmitted through sexual contact.
Sometimes STIs may not cause symptoms (asymptomatic STIs), but even if there are no symptoms, your health can be affected, and you can pass the infection on.
How do you prevent getting infected?
Thinking or hoping a sexual partner doesn’t have an STI is no protection – you need to know for sure. And although condoms, when properly used, are highly effective in reducing transmission of some STIs, no method is fool proof.
The only reliable way to avoid infection is to not have any anal, vaginal, or oral sex.
What causes STIs?
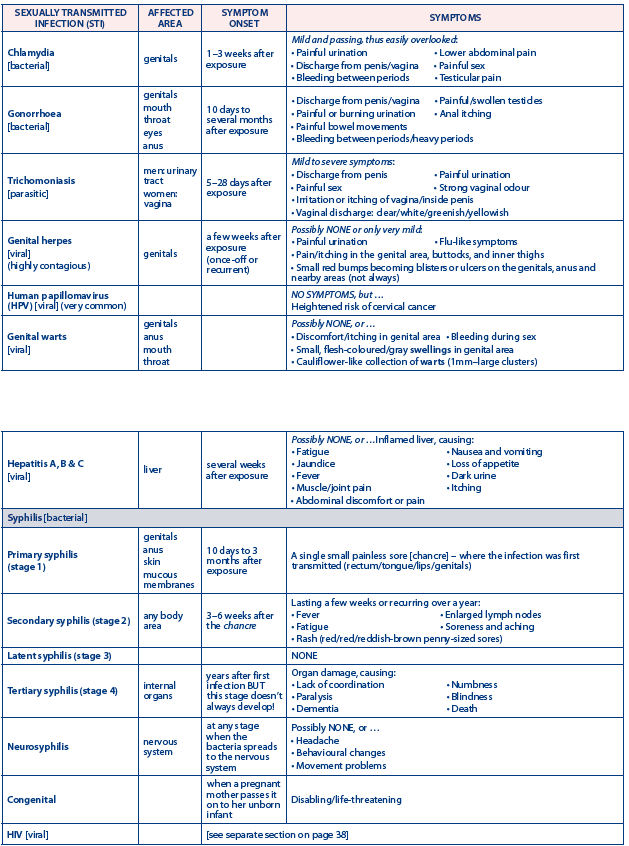
STIs are caused by bacterial, yeast, parasitic or viral infections. There are more than 20 types of STIs. Antibiotics can treat STIs caused by bacteria, yeast, or parasites. There is however no cure for STIs caused by a virus, but medicines can often help with the symptoms and keep the disease under control. Some of the most common types of STIs include:
chlamydia
gonorrhoea
genital herpes
human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
human papillomavirus (HPV)
syphilis
What happens when an STI goes untreated?
If untreated, STIs can increase your risk of acquiring another STI such as HIV. This happens because an STI can stimulate an immune response in the genital area or cause sores – either of which might raise the risk of HIV transmission. Some untreated STIs can also lead to infertility, organ damage, certain types of cancer or death.
STI symptoms aren’t always obvious. If you think you have STI symptoms or if you think you may have been exposed to an STI, see a doctor immediately. It’s essential to be evaluated, and – if diagnosed with an STI – get treated. It’s also essential to inform your partner so that they can be evaluated and treated.
Who is most vulnerable to contracting an STI?
The following factors increase the risk of getting an STI:
having more than one sexual partner
having a sexual partner who has or has had more than one sexual partner
having sex with someone who has an STI
having a history of STIs
using intravenous drugs (injected into a vein) or having a sexual partner who uses intravenous drugs